Executive Summary
The major objective of this market plan is to guide the decision making process of Luckin’s B2B marketers to attract business partnership and investment in China’s market. So far, China’s Coffee Shop Industry is more occupied by Starbucks, Costa and other foreign large chain stores. In order to increase the market share and convince potential partners that Luckin’s services are competitive and profitable, Luckin Coffee has to develop effective B2B marketing plan. The major B2B businesses of Luckin is chain stores and vending machines.
1.0 Introduction 1
2.0 Macro Drivers 2
3.0 Competitive analysis 3
4.0 Segment Analysis 6
5.0 Marketing Mix 7
Reference 11
1.0 Introduction
Coffee is one of the fastest growing segments of the beverage sector in China. As shown in figure 1 below, the coffee shop industry market size in China this year is predicted to be almost three times larger than it was in 2013. it shows that China’s coffee shop industry is filled with opportunities for coffee shop owners.
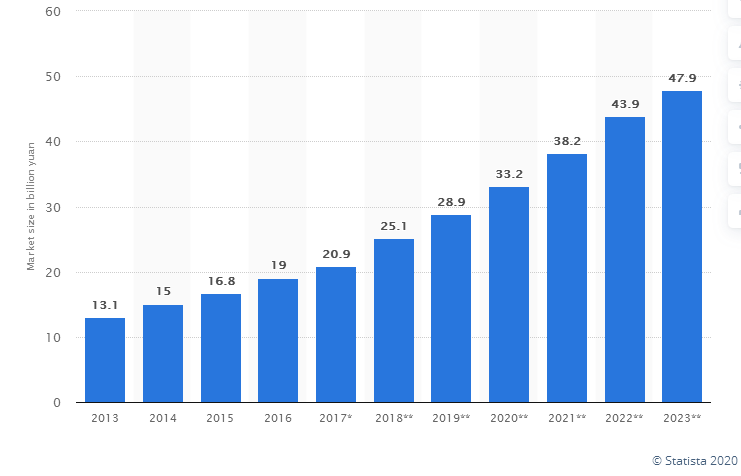
Source Credit: Statista, 2020
Fig 1:Coffee shop industry market size in China 2013-2023.
Luckin Coffee was founded by Jenny Qian Zhiya in October 2017. It is currently headquartered in Beijing, China. Luckin Coffee was taken to an IPO with a valuation of $4.2 billion(Picker, 2019). Not only within China’s market, Luckin Coffee competes vigorously with very strong competitors such as Starbucks on the global arena. It now has over 3,700 stores in the global market and only ranks after Starbucks with 4,125 stores(Statista, 2020). However, as a new company, it will still take time for Luckin Coffee to compete and outperform Starbucks in the local market. Therefore, in this report, a detailed market plan will be proposed to help Luckin Coffee to understand the demand of target customers and seize more market share in China.
2.0 Macro Drivers Analysis
PEST model is often used in a macro-environmental drivers analysis. PEST stands for political, economic, socio-cultural and technological factors.
At the political level, China is a totalitarian state ruled by China’s Communist Party or CCP (Lawrence&Martin, 2013). Even though it is not a democratic country, China has been run efficiently by the party. High political stability can be assured for Luckin Coffee and other coffee shop owners. Business activities are strictly regulated by the Ministry of Commerce, China.
At the economic level, China’s GDP per capita (PPP) keeps increasing from USD$9,000 in 2010 to $16,186 in 2018 (Tradingeconomics, 2020). It implies that Chinese customers get richer and richer. In other words, it is more feasible for them to afford consumer goods and services.
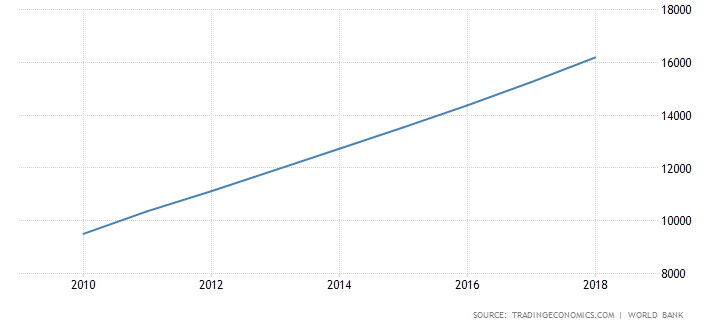
Source Credit: World Bank
Fig 2: China’s GDP per Capita (PPP) from 2010 to 2018
At the socio-cultural level, China’s coffee consumer market is also developing very fast. Now only in developed cities but also in less-developed areas, Chinese consumers especially working professionals aged from 20 to 40 are gradually influenced by coffee culture. Traditionally, Chinese consumers are more favoring tea as compared with other beverages. But recently, coffee becomes more popular among young employees, office ladies and other working professionals. It is because the beverage can help them feel refreshed and more prepared for work.
At the technological level, mobile payment technology boosted by Ali Pay and WeChat Pay is developing very fast. Literally speaking, China is now marching toward a cashless society. When consumers consume their coffee in a coffee shop or quick-service restaurant, it is no longer necessary for them to queue up. They can order coffee and make a payment from their apps. It tremendously saves time for them.
3.0 Competitive Analysis
3.1 Industrial Trend and Market Structure
As shown in figure 3, Starbucks undoubtedly rank the top in China’s coffee chain market. It occupies 80.7% market share. Luckin Coffee’s ultimate goal is to replace Starbucks as the largest coffee chain in China’s market.
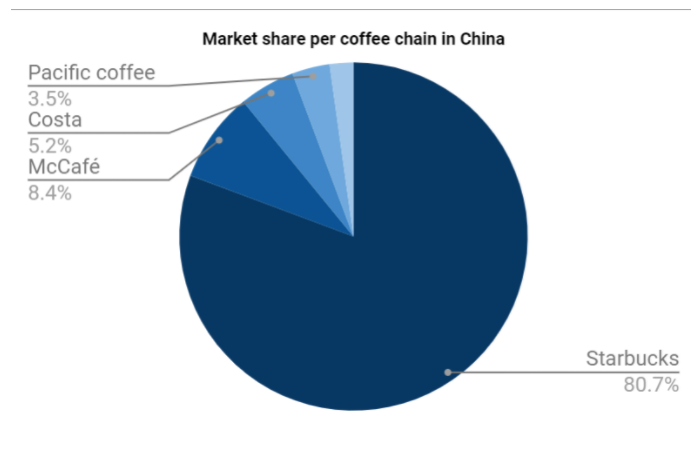
Source Credit: Statista, 2020
Fig 3: Market Share Per Coffee Chain in China
From figure 4, the total number of cup of coffee per year on a per-capita basis of China is only 3. it is much smaller as compared with the U.S and U.K markets. But it also implies that China’s market has a huge growth opportunity for Luckin and other start-up coffee chains. Through taking the advantage of cost-effectiveness in production, it is feasible for Luckin Coffee to take over market shares from Starbucks and other potential competitors.
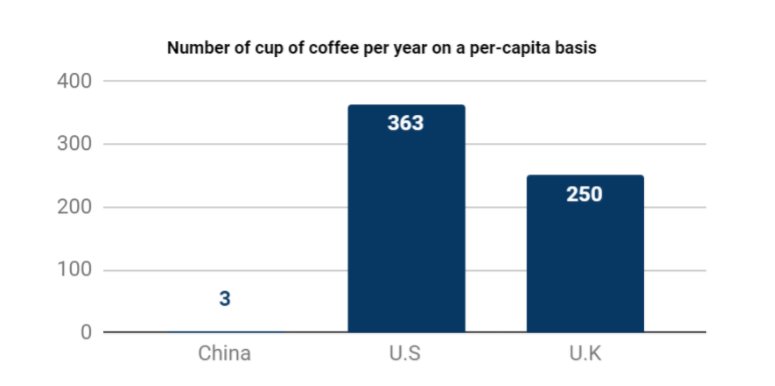
Source Credit: Statista
Fig 4: Number of Cup of Coffee Per Year on a Per-capita Basis
3.2 Competitor Overview
As shown in figure 3, it can be observed that Luckin has four major competitors, including Starbucks, McCafe, Costa and pacific coffee. Apparent, Starbucks is now the largest competitor who has over 80% of market share in China’s coffee shop market(Chuang, 2019). Apart from the major competitor, Luckin also has a replacer, named HeyTea. Like the aforementioned, coffee and tea can be consumed interchangeably among Chinese consumers. Therefore, the competitor analysis should consider both Starbucks and HeyTea.
Table 1: Comparative analysis among Luckin, Starbucks and Heytea
Company |
Luckin Coffee |
Starbucks |
Heytea |
Size |
3,700 stores |
4,125 Stores |
3,000 stores |
Market share |
5% |
80.7% |
34% * (Milk Tea Market) |
Business Model |
Coffee Network |
Company-operated Chain business |
Chain business |
Operating Strategy |
Ø Affordable Coffee Product |
Ø High-quality customer service and experience |
Ø Tea products with innovation and creativity Ø Target at youth
|
The major differences among Luckin, Starbucks and Heytea can be viewed from the table above(Ferreira&Ferreira, 2018). Luckin has opened more than 3,700 stores in the world but has a much smaller market share as compared with Starbucks. Besides, Heytea as compared with Luckin has a much better performance in the milk tea market. The business model of all the three stores is chain business. The major difference is that nearly 80% of Starbucks stores are company-operated. HeyTea, on the contrary, does not have company-operated stores. Each HeyTea store is operated by individual business owner. Luckin more positions itself as a place for people to fresh and relax themselves. So it is more a coffee network rather than a coffee chain store. All of the chosen stores have advantages and disadvantages in the business operations. Luckin makes its coffee products more affordable to customers. But the disadvantage is that some customers may look for high-end products. In other words, they are not very price sensitive. They care more about the quality of the products. Starbucks, on the other hand, targets at customers from high-income group. Through providing high-quality customer services, it is feasible for the company to earn more revenue as compared with the other two. But one problem is that the price of Starbucks’ products are much more expensive. Price-sensitive customers may be screened out due to the high price. HeyTea is widely loved by Chinese youth but the problem is that people from other age groups are less interested in HeyTea’s products.
3.3 Perception map
As compared with Starbucks, Luckin coffee tends to have acceptable quality but a much cheaper price. HeyTea also has the same features. HeyTea’s products are perfect substitutes of Luckin’s coffee.
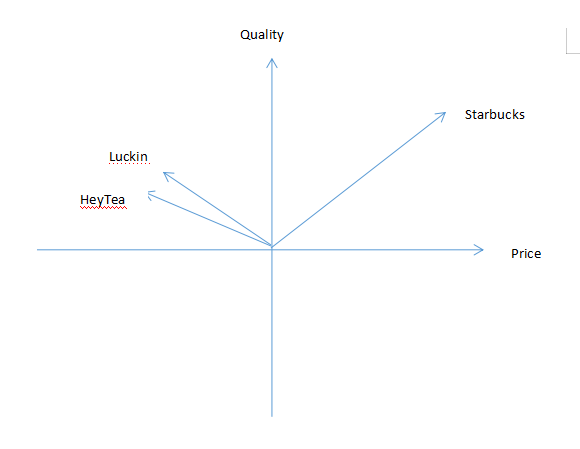
Fig 5: Perception Map
4.0 Segmentation Analysis
4.1 B2B Market Segmentation
B2B and B2C marketing target at very different audiences. B2B is actually making buying decisions for companies instead of individual customers(Hadjikhani&LaPlaca, 2013). B2B marketing intends to create demand and high-quality leads instead of developing brand awareness, popularity or loyalty. Target audiences of B2B marketing expect look for increased business value. In the B2B market plan for Luckin Coffee, the major B2B audience is the individual business owners who are attracted by Luckin’s culture, product features and vision and willing to become Luckin’s business partners as part of the chain business. The primarily targeted business partners are Chinese individual business owners and investors who have interests in starting coffee shop businesses. The second type of B2B partners are individuals who are willing to invest in Luckin’s vending machines that allows customers to purchase hot beverages and snack products(Picker, 2019).
4.2 Blue Ocean Strategy
By definition, Blue Ocean Strategy (BOS) is a tool to avoid costly competition through innovation with the aim to create a market where no firms currently operate, leaving the company to expand without competition(Kim, 2005) . To make it simple, it means that company now plays the critical role in creating a new market. On the opposite, red ocean means that companies are actually competing fiercely with one another to seize market share. There are two dimensions in the BOS including the reduction of cost and value increase. On one hand, Luckin coffee can access the cheap labor, low land cost and energy cost to reduce the cost of production. On the other hand, Luckin Coffee also discovers that value can be increased for potential business partners. As China’s coffee shop market is filled with business opportunity, business partners can be attracted by Luckin’s business model, that is, to provide affordable coffee products for working professionals and young people. From the perception map, Starbucks, the major competitor of Luckin, has a very different marketing position. It is feasible for Luckin’s partners to jointly enjoy business success through opening Luckin Coffee chain stores or operating vending machine.
5.0 Marketing Mix - Product and Pricing
5.1 Product Strategy
Ø Product Life Cycle:
The product life cycle concept is derived from the fact that a given product’s volume and revenue follow a typical pattern of four-phase cycle, including introduction, growth, maturity and decline, as shown in fig 6 below(Jüttner, Godsell &Christopher,2006). Now Luckin Coffee is at Phase Two in the product life cycle or PLC. As compared with a B2C marketing strategy, service proposition of B2B marketing is to highlight the business value and develop trust with potential business partners. Hence, the major marketing strategy is decided to be rapid penetration. It is a strategy to launch Luckin services at a low price with heavy promotion.
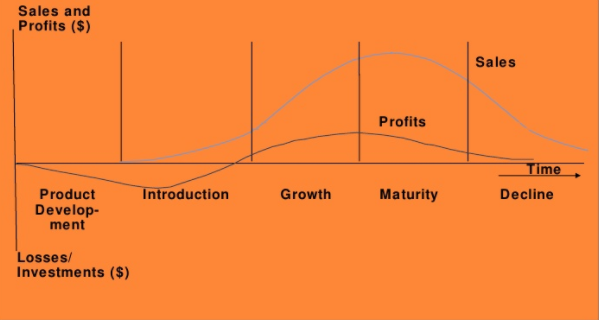
Source Credit:Jüttner, Godsell &Christopher,2006
Fig 6: Product Life Cycle of Luckin Coffee
Ø Product Portfolio Strategy:
As part of the B2B marketing strategy, it is important for luckin in to analyze the portfolio or collection of products. The product portfolio is often depicted by the Boston Matrix as shown in the figure 7 below. Luckin currently has low market share but has high market growth. B2B investors tend to feel that Luckin Coffee does have business potential but the future is still uncertain. One potential product portfolio strategy is to increase the market share of Luckin Coffee in China’s market. When the market share of Luckin is increased, investors can be convinced that Luckin is a reliable business partner(Kang& Montoya, 2014).
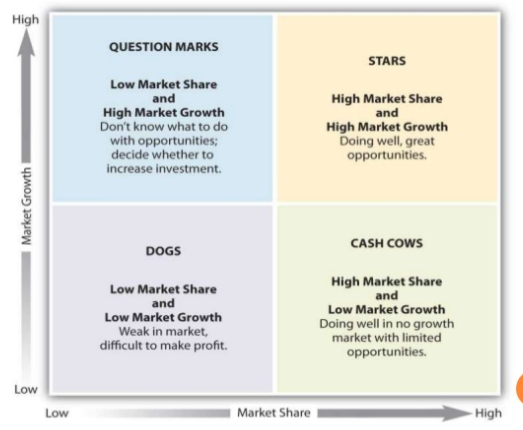
Source Credit:Konečný & Zinecker, 2015.
Fig 7: Boston Matrix
Ø Product Level Model:
Customers will choose a product according to its perceived value. The Five Product levels model is often used to show that a product can be more than just a tangible entity(Kotler, 2012). It can be identified based on the five levels as shown in Fig 8. The core benefit is the fundamental need or wants that the customer satisfies when they buy the product. The core interest of a B2B client is to earn profits from the business partnership or investment. Generic product means that the basic version of the product is made up of only those features necessary for its function. For instance, vending machines can be used to sell the Luckin coffee. Apart from the two above, expected product is the set of features that the customers expect when they buy the product. Luckin’s B2B clients expect that Luckin coffee could have more market share through selling affordable coffee to Chinese customers. Augmented product refers to any product variations or services that help differentiate the product from competitors. In other words, B2B clients want to know what is the major product features of Luckin as compared with major competitors such as Starbucks. Last, potential product includes all augmentations and transformations the product of Luckin might undergo in the future.
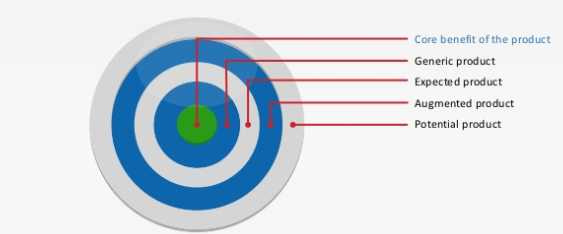
Source Credit: Kotler, 2012
Fig 8: Kotler’s Five Product Model
5.2 Pricing Strategy
Even though in Luckin’s B2C sector, the company is employing a cost-based pricing strategy. Through taking the price leadership, Luckin coffee wants to take over more market shares from other competitors such as Starbucks. However, in the B2B sector, Luckin does not want to attract price-sensitive business partners. Instead, perceived-value pricing strategy is undertaken to attract partners or investors who are attracted by Luckin’s unique culture and values(Sweeney &Soutar, 2001). Luckin aims to produce high-quality coffee product with affordable price and targets at young working professionals. Partners who find business potential in the target market can be convinced that Luckin’s products are highly competitive. Through effectively addressing the perceived value of B2B clients. Luckin can also charge a relatively higher price for business partnership. Besides, low-end and price-sensitive clients will automatically be screened out.
6.0 Marketing Mix: Promotional Strategy
The five-stage Gantt Chart for Luckin Coffee is designed as shown in figure time. “2”, “3”, “4” are three milestones to access the effectiveness of the implementation of Luckin’s promotional marketing strategy. The major promotional strategy is AIDA model (Awareness-Interest-Decision-Action).
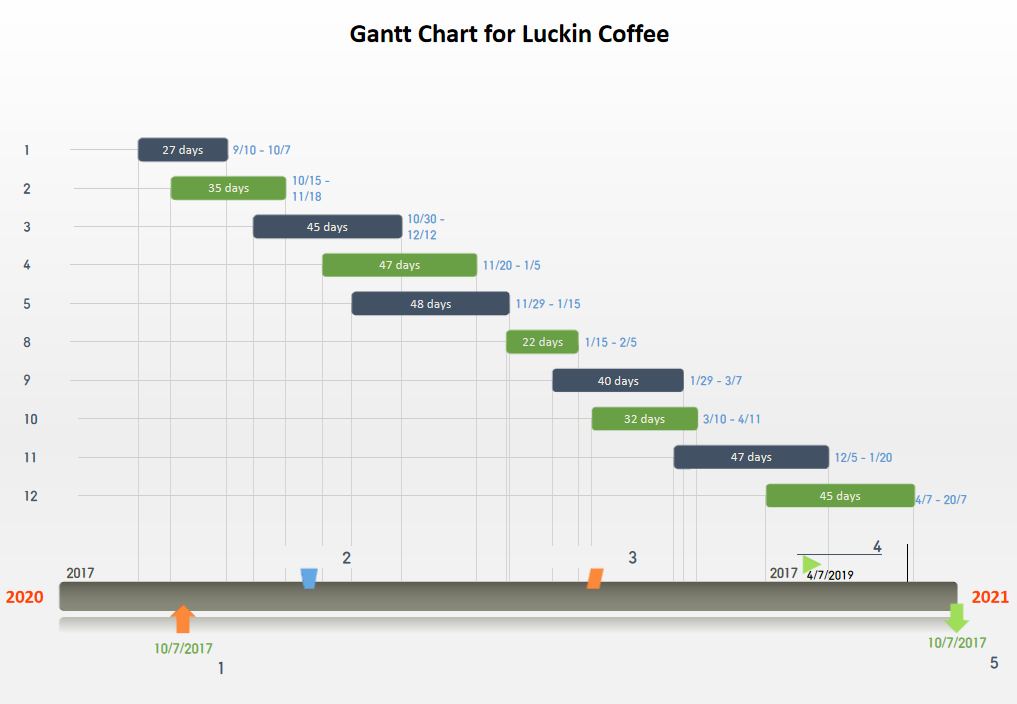
Fig 9:Gantt Chart
List of References
Chuang, H. J. (2019). Starbucks in the World. Holistica. Journal of Business and Public Administration, 10(3), 99-110.
Hadjikhani, A., & LaPlaca, P. (2013). Development of B2B marketing theory. Industrial Marketing Management, 42(3), 294-305.
Ferreira, J., & Ferreira, C. (2018). Challenges and opportunities of new retail horizons in emerging markets: The case of a rising coffee culture in China. Business Horizons, 61(5), 783-796.
Jüttner, U., Godsell, J., & Christopher, M. G. (2006). Demand chain alignment competence—delivering value through product life cycle management. Industrial marketing management, 35(8), 989-1001.
Kim, W. C. (2005). Blue ocean strategy: from theory to practice. California management review, 47(3), 105-121.
Kang, W., & Montoya, M. (2014). The impact of product portfolio strategy on financial performance: The roles of product development and market entry decisions. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31(3), 516-534.
Kotler, P. (2012). Kotler on marketing. Simon and Schuster.
Konečný, Z., & Zinecker, M. (2015). Using the Boston matrix at identification of the corporate life cycle stage.