Module Name:
Assessment Number:
Name:
Student ID:
1.0 Introduction
Great Wall Motor(GWM) is currently China’s largest SUV manufacturer. It has three major brands, namely Great Wall, Havel and Wey. It was founded and now headquartered in Baoding, Hebei province, China in 1984. In 2016, it sets a national historical sales record of selling more than 1 million vehicles worldwide(Great Wall Motors, 2017). The annual sales has dramatically increased by approximate 25% in the following year(Great Wall Motors, 2017). It shows that GWM has enjoyed significant business success in both domestic and global automotive market. The company’s vision is to become the largest SUV producer in the world (See Appendix 1). It is true that GWM has achieved major business success in China’s automobile market but it may face tremendous challenges, uncertainties and difficulties when competing with other automobile producers in the global arena. Therefore, it would be highly necessary and essential for GWM to employ effective management strategies to guide the directions and specific scopes over the long-term within a challenging business environment. Strategy itself is rather an ambiguous term but it is closely associated with every function of a company or an organization to effectively allocate its strategic resources and capabilities to achieve cost and competitive advantages over other major competitors in the local and global market(Lepak, Liao, Chung&Harden, 2006). Strategic human resource management is one of the most important and effective strategy to facilitate the integration of organizational functions into strategic management process (Daley, 2012). Hence, the major purpose of this SHRM report is to assist GWM headquarters to develop and implement effective SHRM strategy in their management process and help the company to gain more sustainable competitive advantages in the long run.
2.0 Evaluation of Strategic resources, capabilities and competitive Advantages
From the Resource-based view (RBV), The relationship among strategic resources, capabilities, management strategy, competitive advantage and the overall business performance could be illustrated in the diagram below.
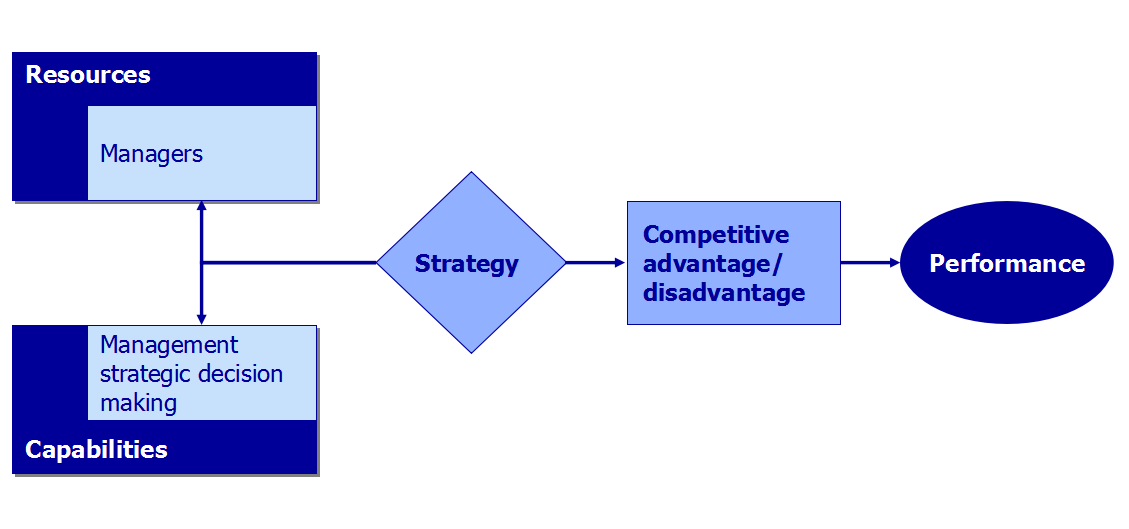
Source Credit: Resourcegate.net
Fig 1: Relationship diagram of Strategic resources, capabilities, strategy, competitive advantages and business performance
2.1 Strategic Resources
Resources are referring inputs that a firm or an organization use to create goods and services. Strategic resources may include tangibles, intangibles and human resources. In GWM, for tangibles, GWM has production facilities mainly in Baoding, Hebei province. According to GWM’s annual report, the Baoding’s factory has a production capacity of 800,000 unites per year(GWM, 2017). Besides, it also has well-accomplished integrated manufacturing lines which allows GWM to enjoy backward vertical integration. In other words, it does not need to purchase intermediate products from third party or pay higher price for raw materials to assemble final automobile products. Based on Porter’s five-force model, backward vertical integration will significantly reduce the supplier power and effectively reduce the production cost for GWM. Moreover, in order to enhance the production capacity to meet the demand of domestic market, GWM decides to set up another manufacturing factory in Tianjin, a direct-controlled municipality of China. The net product capacity is expected to reach 1,000,000 unites per year.
Intangibles are referring to long-term resources which do not exist in physical forms. Typical intangible resources may include organizational culture, reputation, intellectual properties and so on. According to the Annual Report 2017, GWM’s organizational culture has created a fair, simple and transparent work environment with the aim to promote sustainable and healthy development (GWM, 2017). Besides, GWM also has very strong brand value. It could be observed from its significant sales increase as the aforementioned. So far, GWM remains as China’s largest SUV and pick-up truck producers. In addition, GWM is also focusing on developing and innovating its vehicle products. In 2010, GWM constructed its first technical and research center in Baoding. Now it has R&D center in Japan, Bangalore and India. It has intellectual property in engines, door locks, airbags and so on.
Besides, in 2017, GWM is estimated to have a total of 68,000 employees (GWM, 2017). This number is expected to increase to 71,000 by the end of 2018. GWM has high quality of employees who have rich background knowledge, skills and experience in the automotive industry. Employees are motivated to accomplish their job scopes by a unique Remuneration system. Qualified employees will receive bonuses, cash awards and promoting opportunities based on a regular individual performance evaluation.
2.2 Strategic Capabilities
Strategic capabilities is a firm’s skill in using its resources to produce goods and services. Capabilities could be viewed as a bundle of assets or resources to perform business process. In fact, all firms have their own capabilities. Product develop process, for instance, includes product design, pilot testing, process debugging and so on. GWM’s major capability is to produce automobile products with a relatively low cost. It is coherent with the company’s strategy. As GWM is focusing on a low cost strategy, it tries to adopt a backward vertical integration approach to reduce the production cost. It also keeps on improving manufacturing process to remove wastes and promote lean operations. The cost advantage could be viewed as GWM’s major capability or core competency.
2.3 Sustainable Competitive Advantages (SCA)
Competitive advantages occurs when a company or an organization has developed unique or inimitable attributes which significantly outperform the other major competitors in the business. According to the annual report 2017 of GWM, major sustainable competitive advantages could be discovered in six areas(GWM, 2017). First, GWM has a sustainable and healthy working environment established upon the principle of “Enhancing cooperation with integrity and seeking development through cooperation”. In other words, team cohesion and teamwork spirit is promoted among different work groups. Positive organizational cultural will significantly ehance employees’ productivity and work efficiency. Moreover, as the aforementioned, GWM has a core competency in terms of low production cost. This capability is imperfectly inimitable as not very many automakers could implement backward vertical integration. GWM has a good access to raw materials and has the capability of producing intermediate products and assembling the final goods. Thus, it allows GWM to produce value through its low-cost strategy. Customers could enjoy more affordable prices offered by GWM. Last, GWM also has sustainable competitive advantage in terms of technological innovation. So far, GWM has IPs in terms of airbags, door locks and engine design. The huge revenue collected from remarkably good annual sales from all customer segments allow GWM to boost its R&D activities. Other companies are not financially possible to invest heavily in R&D and thus loose the competitive advantages to GWM.
3.0 Other Organizational Contextual Analysis
3.1 Macro-environmental and external Context
PEST is a commonly used contextual analysis tool to help a company or an organization to have a understanding about the external environment of a certain industry. As GWM has gained major business success in local market, it is important for it to learn more about the political, economic, socio-cultural and technological factors in the global market (See Appendix 3).
Politically, major automotive markets in the world have very high political stability. According to the report published by the World Bank, the political stability of the U.S, Canada, Australia, for instance, are ranked the 75th , 20th and 38th place in the world(World Bank, 2018). It is because developed countries have accomplished political system, legal system and stable government. High political stability will reduce the risks of doing business or making investment in a foreign market. Besides, China’s automobile companies are financially supported and subsidized by the Central government. It is because the tax revenue collected from international trade in the global automotive market will contribute to China’s net GDP growth.China’s government also purposely reduces the export tax of Chinese automobile companies. It will make GWM’s products more price-competitive as compared with other competitors. Moreover, governments in foreign markets do provide subsidies and tax reduction policies if an automobile producer is producing environmental-friendly products. For instance, hybrid cars and EVs are subsidized even in a foreign country like the U.S. However, GMW may suffer from high tariffs or income taxation especially when doing business in the U.S. President Trump holds a conservative view about international trade. The protectionism caps may drive up the business cost of GWM. Last, different countries also have very different GHG emission standards. In order to do business in a foreign market, GWM has to do pre-market researches and make sure that the products fulfill the requirements in a foreign country.
Economically, the China’s currency is much weaker than the U.S. As shown in the figure 2, since April 2018, the Chinese Yuan keeps weakening against U.S dollars. It allows China’s enterprises to gain an unfair advantages by making their exported products cheaper than the local goods. In addition, as the world’s economy is gradually recovering from the global financial crisis, even developed countries such as the U.S has enjoyed a slight economic growth. Furthermore, potential markets in developing markets are emerging very fast. Vietnam, for instance, has enjoyed 12% economic growth this year. It shows that GWM should also focus on promoting and selling their products in these emerging markets.
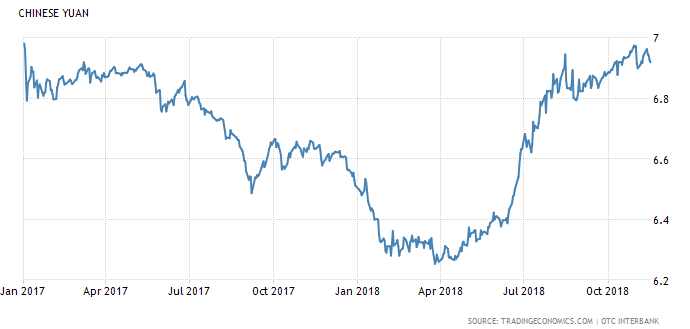
Source Credit: OTC Interbank
Fig 2: U.S dollars against Chinese Yuan
Socio-Culturally, people in the world start to realize the importance of sustainable development. For instance, they are worried that the global warming may lead to the rise of sea level and threaten their lives. In other words, environmental-friendly options such as hybrid cards or EVs will become the future mobility trend. Moreover, there is also a noticeable trend of income gap widening in major automobile markets. GWM has to carefully conduct market segmentation in order to meet the demand of different income and social groups.
Technologically, as the aforementioned, hybrid cars and electric vehicles will be more popular among target customers. It requires automakers to improve the energy storage capacity of EV batters. In addition, as more and more people are used to do their daily activities with their smart phone devices, it is also necessary for GWM to develop more mobile-based functions in their vehicles. For instance, users should be able to remotely adjust the temperature of their cars through apps.
3.2 Micro-environmental and internal Context
SWOT analysis would be an effective tool for GWM to know more about the internal environment, including strength, weakness, opportunities and threats in its business(See Appendix 4). As the aforementioned, GWM is China’s largest SUV producers. It has the largest market share in the domestic automotive market. Besides, the excellent sales performances indicate that it has strong brand value and loyalty among Chinese customers. Besides, it also has a good brand reputation for producing relatively cheap price with promising product quality. Apart from high brand values, GWM also has an easy access to various financing channels. First, GWM is financially supported by China’s local government as it can generate jobs for thousands of Chinese people. Good Balance of Payment records also allows GWM to have sufficient budget to invest in its R&D projects. However, GWM does have very significant weaknesses it its business operations and activities. First, it lacks product variety and diversification. So far, the major product of GWM is still SUV. As compared with other brands, it does not have plentiful choices or models for customers to choose. Moreover, it tends to have low marketing positioning and almost no market segmentation strategies. GWM tries to gain market share through its cost-leadership strategy but it also means that it focuses on low-end customers by providing them with low price vehicles. However, GWM should not abandon the high-income groups as they might be more profitable. Especially when GWM is promoting products in a foreign country, GWM has to prove that it can also produce high-end vehicles. Also, GWM is technologically relying on other automobile companies. For instance, some GWM’s products have to use Mitsubishi engines and Siemens electronic systems.
As the aforementioned, GWM could explore business opportunities in the global market. As more and more countries and customers are favoring hybrid cars and EVs, GWM should try to develop more electric vehicle products. It is also easier for GWM to receive financial grants from local government. Moreover, as GWM is competing with automakers such as Toyota, Ford, Fiat, and so on, in the global market, its cost leadership strategy will certainly help GWM to gain competitive advantage over the other companies. However, the major threats are the vigorous competition with other automobile giants. The global automotive market tends to be saturated. It is very difficult for Chinese automakers to compete with other existing brands in terms of product quality and customer base. In addition, the availability of domestic substitutes in terms of low-cost vehicles are also high. Customers could easily switch to other local brands such as Geely, BYD, etc. The cost of switching is low. Hence, the market position of GWM in local automotive industry is not unshakable.
3.3 HRM context
Currently, according to the annual report 2017, GWM is now facing several HR issues and challenges (GWM, 2017). At the employee’s level, majority of GWM’s workers are only 30 years old on average. In other words, they might not have sufficient skills and background knowledge to fulfill the requirement of employers in respective production activities. Last year, GWM launched “the Accurate Poverty Alleviation Plan” to provide job opportunities for people who lived in remote and impoverished areas. It is also considered as part of GWM’s corporate social responsibility (CSR) strategy. It is true that GWM is providing social benefits and positively externalities to poor and uneducated people especially in rural area but the HR department has to deal with the problem associated with low-skilled labor. If the manufactured products could not meet the customer’s expectation, even loyal customers will switch to other brands. If target customers are continuously dissatisfied with GWM’s products, the net business performance and profit margins will certainly drop.
At the corporate level, the work satisfaction of employees in GWM is also very low. It is also the major reason accounted for the current high turnover rate. In China, GWM is reported to have a very high turn-over rate of 20%. According to the concept of psychological contract, employees are often dissatisfied about their working condition and environment because their internal expectations have not been met by their employers. For instance, some employees may expect them to be promoted as they have accomplished missions or made significant contribution. As the aforementioned, many GWM’s workers are very young. GWM headquarters often assume that young people are not experienced and skillful enough to be qualified in higher position. So the managing team is reluctant to provide them with promoting opportunities. As such, the psychological contract of young employers will be significantly violated. It may further lead to many anti-productive behaviors such as absenteeism. If they are extremely disappointed about their employers, they may quit their jobs straightaway.
4.0 HR Strategies
As the aforementioned, strategic human resource management strategies can facilitate the managing team of GWM to allocate strategic resources and enhance core competencies to gain competitive advantages over other major competitors in both the local and global market. Human resource management strategies could be defined as strategies to effectively manage people to meet a company’s long-term need and expectation(Baker & Doran, 2007). Strategic HRM or SHRM is more about integrating competitive business strategies into human resource management process(Uysal, 2013). Currently, there are three popular SHRM models, including Best Practice, Best fit and Resource based view (RBV) which are widely employed by different companies and organizations(Budhwar & Aryee, 2008). The Best Practice will be developed and introduced into GWM’s context.
4.1 Best Practice
Best Practice, by definition, is a HRM strategy to provide useful services to employees meanwhile generate profitability for employers (Kinnie, et al, 2005). It usually involves a series of functional activities and strategic planning to achieve the above-mentioned HRM goals. Pfeffer (2005) proposes a series of Best Practice strategies including employment security, self-managing team, decentralization, recruiting the right people, etc. Pfeffer (2005) suggests that if a company or organization implements the above-mentioned Best Practice strategies as a holistic measure, the overall organizational performance is expected to increase tremendously. To make the Best Practice model more accomplished, Bacon and Hoque (2005) suggests that compensation schemes, job rotation and flexible working schemes should be introduced into the human resource management process. However, Best Practice model does has its drawback. One potential problem is that Best Practice is over-simplistic, perceptive and lack of concern for real context(Hall & Taylor, 2005). For instance, if employee’s salary is linked to their individual performance, it may result very undesired competition among employees and compromise the team efforts.
But it seems that the Best Practice model could work perfectly well in GWM. As the above-mentioned, GWM’s employees on average are young and unskillful in production and business activities. Under the Best Practice strategy, HR managers could arrange regular training or invite external trainers to upgrade the employees’ skills. It will certainly enhance GWM’s core competencies as well. Besides, through effective job differentiation, employee’s tasks could be simplified into different work packages. It will allow employees to be more capable of accomplishing their tasks. Through holding regular training and job differentiation, the overall productivity of GWM’s workforce is also expected to be enhanced. It will also remove undesired operations in production and business activities. As a whole, the Best Practice strategy is coherent with GWM’s cost leadership business strategy under the Porter’s Generic Competence Model. Through optimizing the manufacturing process, GWM’s workers are expected to generate more and high quality outputs as a consequence.
Moreover, another major problem is about the high turnover rate in GWM. As the aforementioned, the problem of high turn-over rate is due to employee’s dissatisfaction about their working condition and environment. When employees feel that their personal expectations have not been met, psychological contract violation may lead to many anti-productive behaviors and adversely affect the overall productivity. One potential Best Practice strategy could be introducing remuneration policies to reward employees who have made significant contribution or accomplished their tasks. Compensation could be in forms of bonuses, salary increase or promoting opportunities. Employees’ individual performance should be checked regularly through a well-structured performance management system. The remuneration policies do not just act as a monetary compensation for employees but also show that employees’ work are appreciated by their employers. Through the performance management system, employees will also receive feedback from their supervisors. Through effective communication and feedback mechanisms, employees will become more cognizant of employer’s expectations and be more engaged in the production activities.
5.0 Evaluation of HR service delivery
There are many ways an HR function can be structured to deliver effective and efficient services to employees in order to facilitate organizational change or the whole business process. Currently, there are three major HR service delivery model, namely, the centralized model, decentralized model and account management model(Greer, Youngblood&Gray, 1999). In the context of GWM, decentralized HR delivery model should be applied. Currently, GWM has a headquarter-plus-foreign-subsidiary organizational structure. It means that GWM has a headquarter located in Hebei, China and set up several subsidiaries in other China’s major cities and foreign countries. It is obvious that GWM has multiple locations and retail stores. It requires these companies to have decentralized human resource departments. With a decentralized HR service delivery model, GWM’s subsidiaries could have sufficient autonomy and be more adapt to specific business climate in respective locations. According to the Hofstede’s cultural dimensions model, different countries may have very distincitive cultural background(Hofstede, 2010). HR practitioners are expected to deliver corresponding services to address the intercultural differences and facilitate the cross-cultural management. For intance, employees in South Korea is expecting a paternalistic leader who can give them specified tasks. Employee empowerment may not be an effective HR practice there. Decentralized HR delivery is extremely essential when GWM tries to enter the global market.
6.0 Conclusion
In conclusion, this SHRM report is expected to facilitate the managing team of GWM in their decision-making process of selecting appropriate competitive business strategy and human resource management strategy. Through conducting internal and external contextual analysis, competitive advantage analysis, it is indisputable that GWM should be stick to its low-cost strategy when promoting its products in both global and domestic market. Besides, it should also explore more business opportunities in the areas of hybrid vehicles and EVs. In the HRM context, GWM is identified to have two major human resource management problems. The first prolbem is that GWM’s employees are very young and unskillful. The second problem is about the high turn-over rate due to employees’ job dissatisfaction. In order to address the two-abovementioned problems, Best Practice strategy as compared with other SHRM strategies is the most preferrential choice. However, in order to deliver services to emloyees more effectively, a decentralized model should be introduced to allow each GWM’s locations to have sufficient automomy when make critical business decisions.
(Word Counts: 3553)
Reference
Baker, J. and Doran, M. (2007). Human resource management. Lanham, Md.: fRowman & Littlefield Education.
Bacon, N., & Hoque, K. (2005). HRM in the SME sector: valuable employees and coercive networks. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 16(11), 1976-1999.
Budhwar, P. and Aryee, S. (2008). An Introduction to Strategic Human Resource Management. Strategic human resource management : building research-based practice, pp.9-32.
Daley, D. M. (2012). Strategic human resources management. Public Personnel Management, 120-125.
Greer, C. R., Youngblood, S. A., & Gray, D. A. (1999). Human resource management outsourcing: The make or buy decision. Academy of Management Perspectives, 13(3), 85-96.
Great Wall Motors (2017). GWM Annual Report 2017. Retrieved from: http://www.gwm-global
.com/UploadEn/2018/0401/553e4836b83b6802.pdf
Hall, L., & Taylor, S. (2005). Human resource management. Pearson Education UK.
Hofstede, G. (2010). Geert hofstede. National cultural dimensions.
Kinnie, N., Hutchinson, S., Purcell, J., Rayton, B., & Swart, J. (2005). Satisfaction with HR practices and commitment to the organisation: why one size does not fit all. Human Resource Management Journal, 15(4), 9-29
Lepak, D. P., Liao, H., Chung, Y., & Harden, E. E. (2006). A conceptual review of human resource management systems in strategic human resource management research. In Research in personnel and human resources management(pp. 217-271). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Pfeffer, J. (2005). Changing mental models: HR's most important task. Human Resource Management, 44(2), pp.123-128.
Uysal, G. (2013). Stages, Content, and Theory of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM): An Exploratory Study. Journal of Modern Accounting and Auditing, pp.252-256.
World Bank (2018). Political Stability - Country rankings. Retrieved from: https://www.theglobaleconomy.com/rankings/wb_political_stability/
Appendix:
1. Company Profile
Vision statement |
Ø To be the largest SUV producer in the world |
Key goals |
Ø Develop new technology Ø Expand sales volume Ø Electric-powered Vehicles (EVs) |
Values |
Ø High customer satisfaction Ø Effective Human Resource management Ø High product quality with competitive retailing price |
2. Resources, Capabilities and Managerial decisions

3. Organizational Contextual Analysis via PEST
|
Political Ø High political stability Ø Government Subsidy Ø |